Description
Our Chemical & Process Pumps are designed for precision, reliability, and safety in the transfer of corrosive and hazardous fluids.
Manufactured with high-grade alloys, thermoplastics, and engineered seal systems, these pumps ensure leak-free, energy-efficient, and long-lasting operation in even the most demanding process environments.
SMP SYSTEMS provides a complete range of centrifugal, magnetic drive, diaphragm, and vertical pumps, suitable for acids, solvents, alkalis, and viscous fluids.
All pumps comply with CSA, CE, ISO, and ANSI standards, ensuring full safety and environmental compliance across Canada and international markets.
Types of Pumps Offered:
-
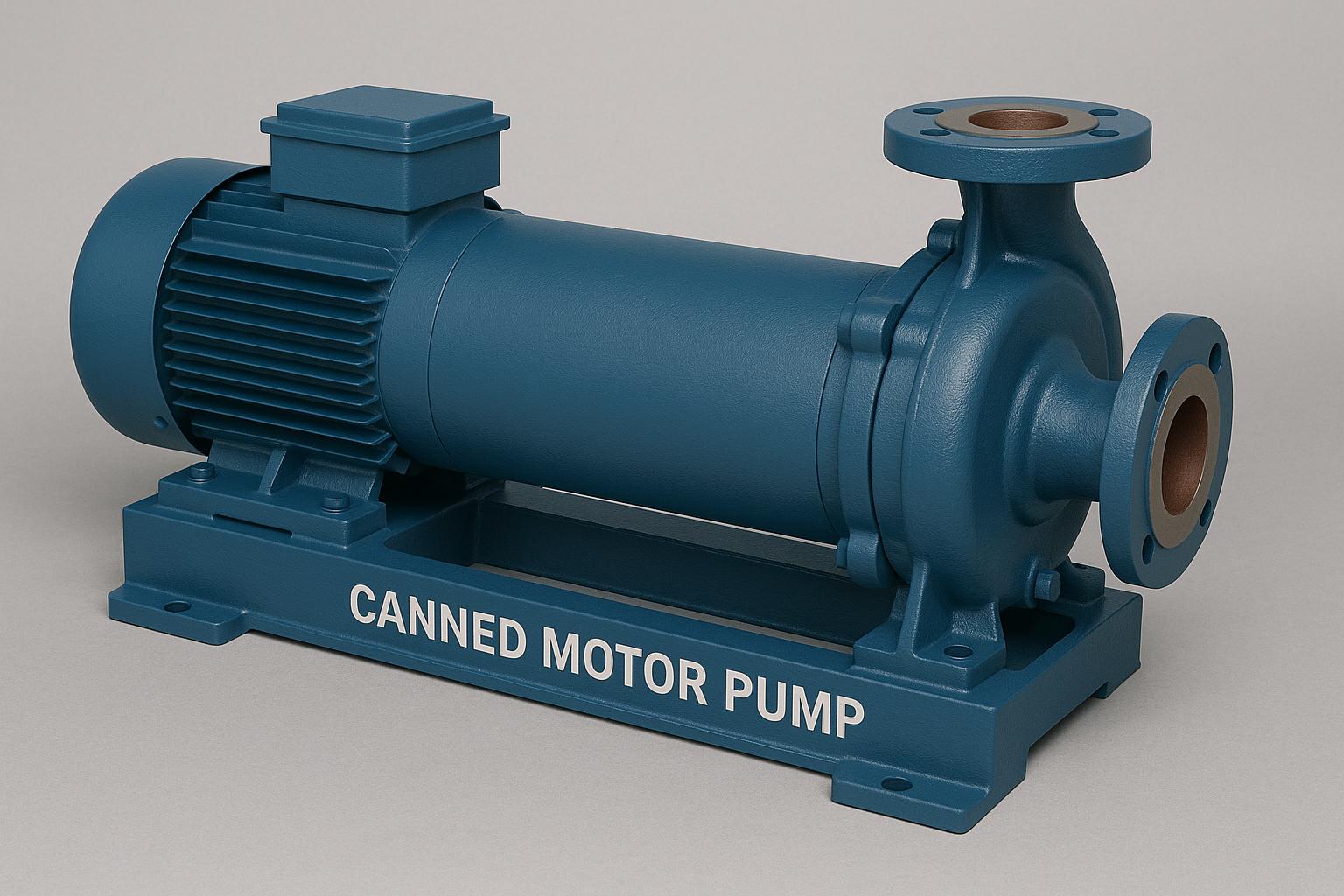
Centrifugal Process Pumps – For general chemical transfer and process flow
-
Magnetic Drive Pumps – Seal-less design for hazardous and toxic fluids
-
Diaphragm Pumps – For precise dosing and corrosive liquid handling
-
Vertical Sump Pumps – For tank and pit installations
-
Self-Priming Chemical Pumps – For easy startup and reliable suction lift
-
PTFE / PVDF Lined Pumps – For highly corrosive chemical resistance
-
High-Temperature Process Pumps – For chemical and thermal applications
Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Pump Type | Centrifugal, Magnetic Drive, Diaphragm, Vertical |
| Flow Range | 10 – 2000 L/min (customizable) |
| Pressure Range | Up to 25 bar |
| Temperature Range | -20°C to +200°C |
| Viscosity Range | Up to 10,000 cP |
| Material of Construction | Stainless Steel (SS304 / SS316 / Alloy 20), PVDF, PP, PTFE, Cast Iron |
| Seal Type | Mechanical, Magnetic Drive, Diaphragm Seal |
| Drive Options | Electric Motor, Pneumatic Drive, Hydraulic Drive |
| Protection Class | IP55 / IP68 (depending on model) |
| Mounting Type | Horizontal / Vertical / Base-Mounted |
Key Features:
-
Excellent chemical and corrosion resistance
-
Leak-free and safe operation with magnetic or diaphragm seals
-
Handles a wide range of acids, alkalis, and solvents
-
Energy-efficient and low-maintenance design
-
High performance in continuous and batch operations
-
Custom configurations for process-specific requirements
-
Complies with Canadian and international safety standards
Applications:
-
Chemical and petrochemical industries
-
Water and wastewater treatment plants
-
Pharmaceuticals and biotechnology
-
Food and beverage chemical handling
-
Pulp and paper manufacturing
-
Acid and alkali transfer systems
-
Paints, dyes, and coatings industries
Certifications & Compliance:
-
CSA Certified – Electrical and mechanical safety for Canada
-
ISO 9001 – Quality Management Systems
-
CE Marking – European conformity
-
ANSI / API 610 Compliance – Process pump standards
-
ATEX Certification – Explosion-proof options for hazardous areas
-
RoHS – Environmentally safe components
-
Health & Safety Standards (Canada/US) – Workplace chemical safety compliant
📩 For product selection, data sheets, or quotation requests, contact us at: sales@smpssystems.com










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.